Supply-Chain Financing
Supply Chain Financing gives added liquidity to buyers.
When buyers demand longer repayment terms, i.e., 120, 180, 360 days, sellers can run into a cash-crunch or simply do not want to take on the risk waiting to be repaid.

There are many structures of supply chain financing, reverse factoring and trade payable financing. For example, supply chain financing companies typically pay those sellers now, with the buyer repaying the financing company at a later date.
After the initial receivable has been extinguished, a debt instrument like, a promissory note, is created in its stead.
Supply Chain Financing optimizes cash flow by allowing businesses to lengthen their payment terms to their suppliers while still allowing a way for the suppliers to get paid early. There are many different ways these are structured. Below are two common examples.
Supply Chain Financing – Promissory Note/Rescheduling of Debt
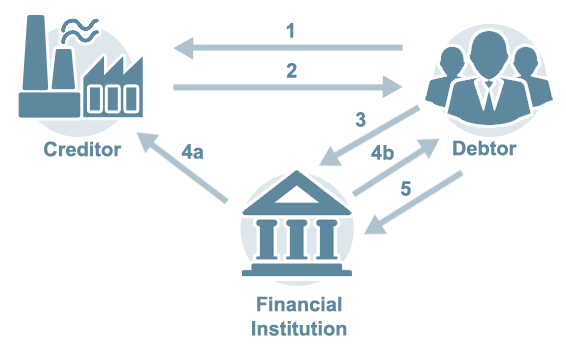
Financial Institution Reschedules Debt, Creates Promissory Note
Credit Insurance Policy Protects Promissory Note
A Promissory Note is a signed document with a written promise to pay a stated sum to a specified party at a specified date; in this type of transaction, the promissory note has a due date that is later than what is specified in the purchase order.
Extended Terms to the Debtor, Freeing up Cashflow
This type of financing provides extended terms to the debtor, freeing up cashflow, while the creditor gets paid within standard terms.
- Debtor sends PO to Creditor
Standard terms of sale (example: net 30) - Creditor ships goods and invoices
Standard terms of sale (example: net 30) - Debtor presents payable to Financial Institution
- a. Financial Institution pays creditor within terms (net 30)
b. Financial Institution sends promissory note to debtor with later due date (example: net 120) - Debtor pays financial institution on later (120th) date
Supply Chain Financing – Financial Institution Acts as Intermediary
Financial Institution controls flow of documents and payments
Credit Insurance Policy Protects invoice from financial institution to debtor
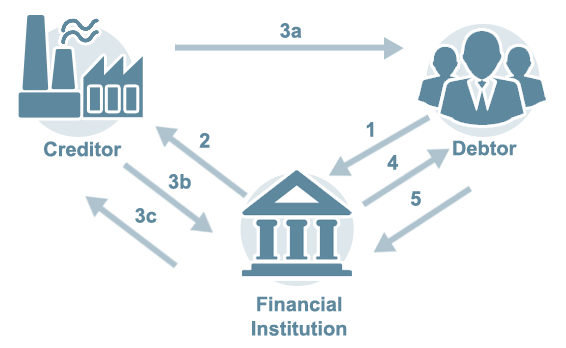
Financing Accords the Financial Institution
This type of financing accords the financial institution with more control over the process, while providing extended terms to the debtor, freeing up cashflow, while the creditor gets paid within standard terms.
- Debtor notifies Financial Institution to place order
- Financial institution issues purchase order on discount terms (example: 1% 10 days/net 30 days) with instructions to ship to debtor
- a: Creditor ships to debtor as per financial institution’s purchase order
b: Creditor issues invoice (example: 1% 10 days/net 30 days)
c: Financial institution pays creditor, takes discount - Financial institution invoices debtor on extended terms (example: net 120 days)
- Debtor pays financial institution on extended due date (120th day)
Working with a specialist can help you determine the best custom solution for your unique needs.
enquiry form
Contact CreditInsurance.com
Frequently asked questions
A. No. Credit life or credit disability insurance is obtained by individuals to help pay debts in case of loss of income. Business credit insurance (also known as trade credit insurance, export credit insurance, or just credit insurance) is used to reduce the risk of non-payment in B2B transactions and is obtained by the company offering the goods or services, rather than the company receiving the goods or services.
A. There is no additional fee to use a broker. By law, you will pay the same rates for the coverage you choose whether you use a broker or work directly with the insurance company. However, a broker helps you evaluate quotes and implement your new policy. Brokers can also help with mandatory reporting requirements and may help you review future claims submissions.
A. The short answer is yes — because things can change. Business insolvency is predicted to increase due to global events. Evaluating the risk of non-payment requires considerable data collection and analysis. Your broker can help you figure out the right amount of coverage for your situation.
A. Trade credit can help you grow your business. When a business is able to purchase goods or services with trade credit, it frees up cash flow, making it a source of short-term financing. This practice allows the business to potentially expand its market or customer base without the negative impact of running out of cash, potentially putting them out of business. Many trade credit agreements incentivize paying early with a discount, so the business is able to decide whether to pay early at a cheaper price or to take longer to pay at full price — based on both money coming into the business and other expenses that need to be paid.
Enquiry form
Contact CreditInsurance.com
Frequently Asked Questions
A. No. Credit life or credit disability insurance is obtained by individuals to help pay debts in case of loss of income. Business credit insurance (also known as trade credit insurance, export credit insurance, or just credit insurance) is used to reduce the risk of non-payment in B2B transactions and is obtained by the company offering the goods or services, rather than the company receiving the goods or services.
A. There is no additional fee to use a broker. By law, you will pay the same rates for the coverage you choose, whether you use a broker or work directly with the insurance company. However, a broker can be a valuable resource, helping you evaluate quotes, implement your new accounts receivable insurance policy, and navigate mandatory reporting requirements. They may also assist with future claim submissions.
A. The short answer is yes — because things can change. Business insolvency is predicted to increase due to global events. Evaluating the risk of non-payment requires considerable data collection and analysis. Your credit insurance broker can help you figure out the right amount of coverage for your situation.
A. Trade credit can help you grow your business. When a business is able to purchase goods or services with trade credit, it frees up cash flow, making it a source of short-term financing. This practice allows the business to potentially expand its market or customer base without the negative impact of running out of cash, potentially putting it out of business.
Many trade credit agreements incentivise paying early with a discount, so the business is able to decide whether to pay early at a cheaper price or to take longer to pay at full price based on both money coming into the business and other expenses that need to be paid.
However, it also comes with the inherent risk of non-payment. Accounts receivable insurance can mitigate this risk by protecting you from losses due to customer default.

